Introduction

Understanding Titanium Machinability Rating
The titanium machinability rating provides a benchmark for how easily different grades of titanium can be machined compared to other metals. This rating takes into account various factors such as tool wear, cutting speed, and surface finish achieved during machining operations. For instance, what is Grade 23 titanium machinability? It’s essential to grasp these ratings to select the appropriate grade for your project.
Importance of Machining Titanium
Machining titanium is vital across numerous industries due to its lightweight yet robust nature. The aerospace sector heavily relies on titanium components for aircraft structures and engines because they require materials that can withstand extreme conditions while keeping weight down. Additionally, the medical device industry benefits from machining titanium because of its biocompatibility and durability; thus, understanding its machinability becomes paramount.
Common Titanium Grades and Their Properties
Titanium comes in various grades, each with distinct properties that affect their machinability ratings. For example, what is the machinability of Grade 1 titanium? This commercially pure grade offers excellent corrosion resistance but has lower strength compared to others like TI 6Al 4V, which boasts a higher strength-to-weight ratio but presents more challenges in terms of machining efficiency. Familiarity with these grades helps manufacturers make informed decisions when choosing materials suitable for their CNC machining projects.
What is Machinability in Metals?

Machinability is a term that refers to how easily a metal can be cut, shaped, or machined into desired forms using various tools and processes. When discussing titanium machinability rating, it’s essential to understand that this rating can significantly influence manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This section will explore the definition of machinability, the factors that affect it, and how machinability ratings are determined.
Defining Machinability
Machinability encompasses several characteristics of a material that affect its ease of machining, including tool wear rate, surface finish quality, and the amount of power required during machining operations. Is titanium easily machinable? The answer isn’t straightforward; titanium poses unique challenges due to its strength and tendency to work-harden. Thus, understanding the specific properties of titanium grades—like Grade 1 or Grade 23—is crucial for effective machining.
Factors Affecting Machinability
Several factors influence the machinability of metals, including their hardness, microstructure, thermal conductivity, and chemical composition. For instance, titanium’s lower thermal conductivity compared to stainless steel can lead to increased temperatures at the cutting edge during CNC machining titanium processes. Additionally, factors like cutting speed and tool material also play significant roles in determining how easily a particular grade of titanium can be machined.
Machinability Ratings Explained
Machinability ratings provide a quantitative measure for comparing different materials based on their ease of machining. These ratings often involve benchmarking against a standard material—usually free-cutting steel—with higher ratings indicating better machinability. When we ask questions like “What is Grade 23 titanium machinability?” or “What is the machinability rating of TI 6Al 4V?”, we refer to these standardized measures that help manufacturers select appropriate materials for their projects while considering cost implications and production efficiency.
Titanium vs. Stainless Steel: A Comparison

Machinability Differences
Is titanium easily machinable? The short answer is no; titanium has a lower machinability rating compared to stainless steel, which can make CNC machining titanium a bit more challenging. For instance, the machinability of Grade 1 titanium is significantly lower than that of many stainless steels due to its tendency to work-hardening during machining processes. On the other hand, when we look at the titanium machinability rating for alloys like TI 6Al 4V, it varies depending on factors such as tool material and cutting conditions but generally remains less favorable than its stainless counterparts.
Strength and Durability
Both titanium and stainless steel boast impressive strength-to-weight ratios; however, they excel in different applications due to their unique properties. Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and a higher strength-to-weight ratio than most grades of stainless steel, making it ideal for aerospace applications where weight savings are critical. Conversely, while stainless steel may not be as lightweight as titanium, it shines in environments requiring high durability and toughness—attributes that make it a go-to choice for many industrial applications.
Cost Implications
While both materials come with their own price tags, the cost implications of using titanium versus stainless steel can be significant over time. Generally speaking, titanium tends to be more expensive due to its complex extraction process and lower availability compared to common grades of stainless steel. However, when considering long-term benefits such as reduced maintenance costs and enhanced performance (especially in high-stress environments), investing in materials like Grade 23 titanium or TI 6Al 4V might yield better returns despite higher upfront costs.
The Titanium Machinability Rating Breakdown
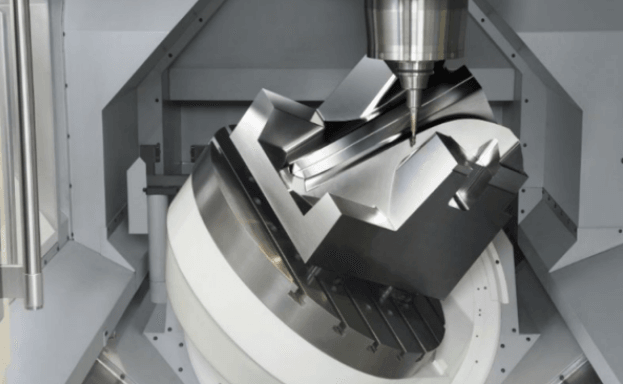
Grade 1 Titanium Machinability
Grade 1 titanium is often regarded as one of the most easily machinable grades in the titanium family. Its high ductility and low strength make it ideal for applications requiring intricate machining processes. So, what is the machinability of Grade 1 titanium? Generally speaking, its machinability rating is favorable compared to other grades; however, proper tooling and techniques are still essential for achieving optimal results.
Is titanium easily machinable? With Grade 1, yes! However, using sharp tools and appropriate cutting speeds will significantly enhance performance during CNC machining titanium processes. Additionally, while it may be easier to machine than some other grades, operators must remain vigilant about tool wear due to its tendency to work-harden.
Grade 23 Titanium Machinability
Grade 23 titanium is a popular choice in medical applications due to its biocompatibility and excellent mechanical properties. But what is Grade 23 titanium machinability like? While it offers a good balance between strength and weight, its machinability rating falls slightly behind that of Grade 1 due to increased alloying elements like aluminum and vanadium.
Machining titanium vs stainless steel can provide insights into how these materials behave under similar conditions. While both materials have their challenges during machining processes, Grade 23 requires more attention when selecting tools and cutting parameters. Operators should expect a bit more effort when working with this grade but will benefit from its superior properties in critical applications.
TI 6Al 4V Machinability Rating
TI 6Al 4V is perhaps the most widely used titanium alloy across various industries due to its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio. What is the machinability rating of TI 6Al 4V? This grade presents more challenges compared to Grades 1 and 23; however, with proper techniques—such as optimizing cutting speeds and using specialized tooling—it's certainly manageable.
CNC machining titanium can be tricky with TI 6Al 4V because this alloy tends to harden quickly when machined improperly. Therefore, understanding how each grade behaves helps operators make informed decisions about tooling strategies when faced with questions like Is titanium easily machinable? The answer varies depending on the specific grade but knowing these nuances can lead you toward successful outcomes in your projects.
CNC Machining Titanium: Tips and Techniques

CNC machining titanium can be a rewarding venture, but it requires the right tools, techniques, and knowledge to navigate its unique challenges. The titanium machinability rating plays a crucial role in determining how easily titanium can be processed compared to other metals. In this section, we will explore the ideal CNC machines for titanium, best practices for machining, and how to troubleshoot common issues that may arise during the process.
Ideal CNC Machines for Titanium
When it comes to choosing the right CNC machine for titanium machining, precision is key. High-speed machining centers equipped with robust spindles are typically preferred due to their ability to handle the toughness of titanium alloys like Grade 1 and Grade 23 titanium. Additionally, machines with advanced features such as rigid tapping capabilities and thermal stability are essential since they help maintain accuracy while reducing wear on tools—especially important when considering the machinability rating of TI 6Al 4V.
Moreover, it's wise to select machines that offer variable speed settings and torque control. These features allow operators to adjust cutting speeds based on specific grades of titanium being machined; for instance, is titanium easily machinable? Not all grades respond similarly under various conditions! Therefore, investing in a high-quality CNC machine designed specifically for metalworking will pay off in terms of efficiency and output quality.
Best Practices for Machining
To achieve optimal results when machining titanium, adhering to best practices is crucial. First off, selecting the appropriate cutting tools is non-negotiable; carbide tools often outperform standard high-speed steel ones due to their ability to withstand heat generated during machining operations. When considering what is Grade 23 titanium machinability? It’s essential to remember that using sharp tools helps minimize friction and prolong tool life while ensuring smoother cuts.
In addition to using quality tools, proper cooling techniques should never be overlooked—titanium generates significant heat during processing! Utilizing flood coolant or mist cooling systems can significantly enhance performance by reducing temperatures at the cutting edge while preventing material from hardening prematurely. Lastly, maintaining consistent feed rates tailored specifically for each grade will ensure effective material removal without compromising surface finish or dimensional accuracy.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even seasoned machinists encounter challenges when working with materials like titanium; however, knowing how to troubleshoot common issues can make all the difference! One prevalent problem involves excessive tool wear—if you notice rapid degradation of your cutting edges while working with materials such as Grade 1 or TI 6Al 4V titanum alloys—consider revisiting your feed rates or coolant application methods.
Another issue could be chatter—a vibration phenomenon that often leads not only to poor surface finishes but also potential damage both on parts being machined and tooling itself! To combat this frustrating occurrence effectively: ensure that workpieces are securely clamped down; evaluate spindle speeds; or even explore different tool geometries suited specifically for machining titanium vs stainless steel applications.
Lastly—and perhaps most importantly—monitoring chip formation is vital during any operation involving CNC Machining Titanium! Poor chip removal can lead directly back into your work area causing scratches or defects; thus keeping an eye out ensures smooth operations throughout every stage of production!
Real-World Applications of Titanium Machining

Titanium machining is not just a technical endeavor; it plays a crucial role across various industries that demand strength, lightweight materials, and corrosion resistance. Understanding the titanium machinability rating helps manufacturers choose the right grade for their specific applications. Let’s dive into how titanium is utilized in the aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors.
Aerospace Industry Applications
In the aerospace industry, weight savings are paramount, making titanium an ideal choice due to its high strength-to-weight ratio. Components such as airframes, engine parts, and landing gear often utilize titanium grades like TI 6Al 4V because of its excellent machinability rating and performance under extreme conditions. Is titanium easily machinable? With proper techniques and equipment, such as CNC machining titanium parts efficiently becomes feasible while maintaining precision.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical devices require materials that are not only strong but also biocompatible—qualities that titanium possesses in abundance. The machinability of Grade 1 titanium is particularly favored for surgical implants and instruments because it can be precisely shaped while ensuring patient safety. Moreover, understanding what is Grade 23 titanium machinability allows manufacturers to select this grade for applications requiring enhanced mechanical properties without sacrificing ease of machining.
Automotive Components
The automotive industry has increasingly turned to titanium for components like exhaust systems and connecting rods due to its ability to withstand high temperatures while remaining lightweight. Machining titanium vs stainless steel presents unique challenges; however, with a good grasp of the respective machinability ratings—like that of TI 6Al 4V—manufacturers can optimize their processes effectively. The result? Enhanced performance vehicles that benefit from reduced weight without compromising on durability.
Conclusion

In summary, understanding the titanium machinability rating is crucial for anyone working with this remarkable metal. While titanium offers exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, many still wonder, Is titanium easily machinable? The answer lies in its grades; each has unique properties affecting their machinability ratings, making it essential to choose the right one for your specific project.
Key Takeaways on Titanium Machinability
For instance, Grade 1 titanium machinability is generally easier compared to more complex alloys like TI 6Al 4V, which has a lower machinability rating due to its higher strength and hardness. Additionally, understanding the differences in machining titanium vs stainless steel can save time and resources—titanium often requires specialized tools and techniques to achieve optimal results.
Future Trends in Titanium Machining
The future of titanium machining looks promising as technology continues to evolve. Innovations in CNC machining titanium are paving the way for improved efficiency and precision, allowing manufacturers to explore new applications across various industries. Furthermore, advancements in cutting tool materials and coatings are likely to enhance the machinability of challenging grades like Grade 23 titanium—making it more accessible for diverse applications.
How to Choose the Right Grade for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate grade of titanium is vital for achieving desired outcomes in your projects. Factors such as tensile strength requirements and environmental conditions should guide your choice; for example, if you need a balance between strength and ease of machining, considering both Grade 1 and TI 6Al 4V can be beneficial based on their respective machinability ratings. Ultimately, understanding what is Grade 23 titanium machinability will help you make informed decisions that align with your project's goals.

