Introduction

In the world of precision manufacturing, CNC milling and turning stand out as two essential processes that shape the way we create complex parts and components. Each method offers unique advantages and capabilities, leading many to wonder, What is the difference between CNC milling and turning? Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in production, as it directly impacts efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the quality of the final product.
Understanding CNC Milling and Turning
CNC milling involves rotating a workpiece against a stationary cutting tool to remove material in various shapes and sizes. On the other hand, CNC turning rotates the workpiece while a stationary tool cuts away material to achieve cylindrical shapes. Both processes utilize advanced technology to ensure precision but cater to different design needs—knowing what is the basic process of CNC turning and milling can help you choose wisely.
Key Differences Between Processes
When comparing CNC milling with turning, it's essential to recognize their operational distinctions: milling typically handles flat surfaces or intricate designs while turning excels at producing round geometries. Additionally, each process utilizes specific tools tailored for their functions; understanding cnc milling and turning tools can enhance your manufacturing strategy significantly. This leads us to ask not only about their differences but also about what is the difference between CNC milling and machining in broader terms.
Importance of Choosing the Right Method
Selecting between these methods hinges on several factors including material type, desired precision levels, and production volume requirements—this decision can make or break a project’s success! For example, if you're working with softer materials or need high-volume runs, you might lean towards one method over another based on efficiency metrics alone. Ultimately, understanding how each process aligns with your project goals will inform your choices in this ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing technology.
What is CNC Turning?
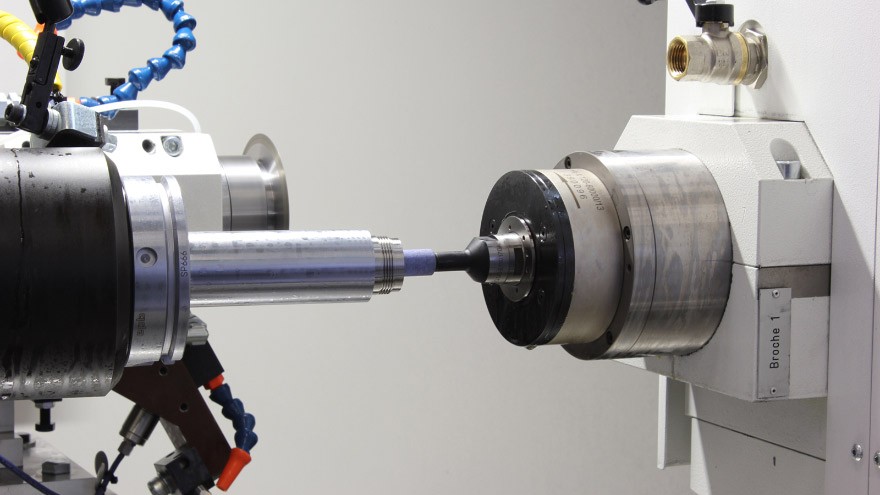
CNC turning is a precision manufacturing process that involves rotating a workpiece against a cutting tool to create cylindrical parts. This method is particularly effective for producing components with rotational symmetry, such as shafts, bushings, and fittings. Understanding what CNC turning entails is crucial for anyone looking to differentiate between CNC milling and turning or explore the basic processes involved in both.
Overview of CNC Turning Process
In the CNC turning process, a computer-controlled lathe spins the workpiece while a stationary cutting tool removes material to achieve the desired shape and dimensions. The process begins with loading the material onto the lathe and setting up the cutting parameters via software. As the machine operates, it meticulously shapes the material into precise geometries, showcasing how CNC technology enhances both efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing.
Key Specifications of CNC Turning
When discussing key specifications of CNC turning, factors such as spindle speed, feed rate, and tooling play vital roles in determining output quality. The spindle speed dictates how fast the workpiece rotates, which can significantly affect surface finish and machining time. Additionally, understanding what is the difference between CNC milling and machining helps clarify that while milling focuses on flat surfaces or complex shapes using rotating tools, turning specializes in creating cylindrical forms with high precision.
Applications of CNC Turning in Industries
CNC turning finds applications across various industries due to its ability to produce high-precision components efficiently. From automotive parts like axles and engine components to medical devices requiring stringent tolerances, this process proves invaluable for manufacturers seeking reliability and quality. By recognizing how these applications differ from those suited for milling—like creating intricate designs—one can better appreciate why choosing between cnc milling and turning tools is essential based on project requirements.
What is CNC Milling?
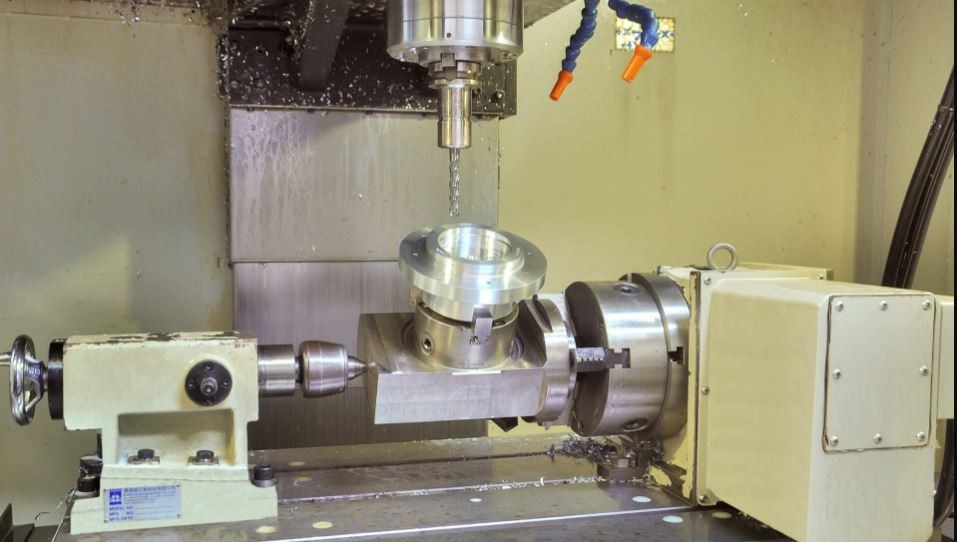

CNC milling is a computer-controlled machining process that shapes materials into desired forms by removing material from a workpiece. This method utilizes rotary cutters to perform various operations, including drilling, boring, and contouring. Understanding CNC milling and turning processes helps manufacturers optimize production efficiency and achieve precise results.
Overview of CNC Milling Process
In the CNC milling process, the workpiece is secured on a table while a rotating cutting tool moves along multiple axes to remove material. The movement can be vertical or horizontal, allowing for complex shapes and designs to be created with high precision. Unlike turning, where the material rotates against a stationary tool, milling involves moving the tool over the fixed workpiece, making it suitable for flat surfaces and intricate geometries.
Key Specifications of CNC Milling
CNC milling machines are characterized by their versatility in processing various materials such as metals, plastics, and composites. Key specifications include the number of axes (typically 3 to 5), spindle speed (measured in RPM), and feed rate which affects how quickly material is removed. Understanding these specifications is crucial when determining what is the difference between CNC milling and machining since they dictate how effectively different tasks can be performed.
Applications of CNC Milling Across Sectors
CNC milling finds applications across numerous sectors due to its adaptability and precision capabilities. Industries such as aerospace use it for creating complex engine components, while automotive manufacturers rely on it for producing intricate parts like gears and housings. Additionally, medical device manufacturing benefits from CNC milling's ability to produce high-tolerance components essential for surgical instruments.
The Milling and Turning Difference Explained

When it comes to CNC machining, understanding the differences between CNC milling and turning is crucial for selecting the right method for your project. Each process has its unique operational structures, material compatibilities, and precision capabilities that can significantly impact the final product. Let’s dive deeper into these distinctions to help clarify what sets these two processes apart.
Structural Differences in Operations
CNC milling and turning operate on fundamentally different principles. In CNC milling, the workpiece is typically stationary while a rotating cutting tool moves across its surface to remove material, creating complex shapes and features. In contrast, CNC turning involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, effectively shaping it into cylindrical forms or contours—this is often where you’ll find the question: What is the difference between CNC milling and turning?
This structural divergence means that each method excels in different applications; for instance, CNC milling can create intricate designs with multiple dimensions while turning focuses primarily on symmetrical shapes like shafts or discs. Understanding these operational structures not only clarifies their functionalities but also determines which process will yield better results based on your specific needs.
Material Types Best Suited for Each Process
The choice of materials plays a significant role in determining whether you should opt for CNC milling or turning. Generally speaking, CNC turning is best suited for materials that are easily machined into cylindrical forms—think metals like aluminum or brass as well as plastics that lend themselves well to this type of processing. On the other hand, CNC milling shines when dealing with flat surfaces or complex geometries found in materials such as steel, titanium, and composite materials.
Moreover, certain materials might perform better under one process than another due to their physical properties; harder materials may benefit from the high-speed rotation inherent in turning operations while softer materials might be more efficiently shaped using milling techniques. Therefore, knowing what is the basic process of CNC turning and milling helps you choose compatible material types effectively.
Precision and Tolerances in Milling vs. Turning
Precision is often a deciding factor when choosing between machining methods—so what’s the scoop on tolerances? Generally speaking, both CNC milling and turning offer excellent precision capabilities; however, they excel under different conditions due to their structural differences mentioned earlier. For example, while both processes can achieve tight tolerances within microns (0.001 inches), CNC milling tends to be favored for applications requiring intricate details because of its ability to manipulate multiple axes simultaneously.
On the flip side, if your project demands high-volume production of uniform cylindrical parts with consistent tolerances over large batches—CNC turning may be your best bet! This understanding of precision levels allows manufacturers to make informed decisions about which method suits their specific requirements best.
What is the Basic Process of CNC Turning and Milling?

Understanding the basic processes of CNC turning and milling is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing or machining. These processes utilize computer numerical control (CNC) technology to enhance precision, efficiency, and repeatability in creating parts. But what exactly happens during these operations? Let’s break it down step by step.
Step-by-Step in CNC Turning
CNC turning begins with securing the raw material, typically a cylindrical workpiece, onto a rotating spindle. The machine then uses various cutting tools that move linearly against the spinning material to shape it into desired dimensions. This process allows for intricate designs, such as grooves or threads, to be created with high accuracy.
The first step involves programming the CNC machine with specific parameters like speed and depth of cut, ensuring optimal performance during operation. Once set up, the machine executes the programmed commands automatically, allowing for consistent results across multiple pieces. Finally, after machining is complete, quality checks are performed to ensure that each part meets specified tolerances—an essential aspect of CNC milling and turning.
Step-by-Step in CNC Milling
In contrast to turning, CNC milling employs a stationary workpiece while rotating cutting tools carve out shapes and features from various angles. The process starts similarly with programming; however, here the focus is on defining tool paths that dictate how cutters will interact with the material. The versatility of milling allows for complex geometries like pockets or contours that would be challenging to achieve through turning alone.
Once everything is programmed correctly into the system, operators can initiate the process which involves multiple axes moving simultaneously for precision cuts. After milling operations are complete—often followed by several passes to reach desired depths—the final product undergoes inspection just like in turning operations to ensure quality standards are met consistently across all units produced.
Comparing Workflow Efficiency
When comparing workflow efficiency between CNC turning and milling processes, several factors come into play including setup time and production speed. Generally speaking, CNC turning tends to have quicker cycle times due to its straightforward approach with cylindrical parts; this makes it ideal for high-volume production runs where consistency is key. On the other hand, while milling may take longer due to its more complex nature involving multi-axis movements and tool changes, it offers unparalleled flexibility when working on intricate designs.
Moreover, understanding what is the difference between CNC milling and machining can help manufacturers choose methods based on their specific needs—turning excels at producing round components while milling shines with flat surfaces or irregular shapes. Both processes also require distinct sets of cnc milling and turning tools tailored for their respective tasks; thus knowing these differences can significantly impact overall efficiency in production workflows.
In conclusion, whether you’re pondering what is the basic process of CNC turning and milling or trying to distinguish between various machining techniques like VMC versus traditional methods—being informed about each will empower you in making better manufacturing choices!
Common Tools Used in CNC Milling and Turning
When diving into the world of CNC milling and turning, it's essential to understand the tools that make these processes possible. Both methods utilize a variety of specialized tools tailored for their specific operations, which can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of the finished product. By recognizing what tools are available, manufacturers can optimize their workflows and ensure they’re using the right equipment for each job.
Overview of CNC Milling and Turning Tools
CNC milling and turning tools are designed to perform precise cuts on a range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. In CNC milling, tools like end mills, face mills, and drill bits are commonly used to remove material from stationary workpieces. Conversely, CNC turning employs cutting tools such as lathes or inserts that rotate around a fixed axis to shape cylindrical parts—this is where we start to see what is the difference between CNC milling and turning.
Understanding these differences helps in selecting appropriate cnc milling and turning tools for specific projects. For instance, while both processes achieve high precision levels, the choice of tool directly influences aspects like surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Moreover, knowing what is the basic process of CNC turning and milling allows operators to better prepare their machinery for different tasks.
Specialized Tools for Different Materials
Different materials require specialized tools to optimize performance during machining operations. For example, harder materials like titanium or stainless steel often necessitate carbide tooling due to its superior wear resistance compared to standard steel bits used in softer materials like aluminum or plastic. This distinction highlights not only what is the difference between CNC milling and machining but also emphasizes how important it is to match your tool with your material.
In addition to material-specific tooling requirements, factors such as heat resistance or chip removal capabilities also dictate tool selection in both cnc milling and turning processes. Using improper tooling can lead to inefficient cutting rates or even damage workpieces—nobody wants a ruined project! Therefore, understanding how various specialized tools function ensures optimal results across different applications.
Notable Brands: SYIL CNC Machines in Action
When discussing cnc milling and turning tools, it’s hard not to mention notable brands like SYIL that have made waves in the industry with their innovative machines. SYIL offers a range of high-quality CNC machines designed specifically for both milling and turning applications—perfect for those looking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities without breaking the bank! Their machines exemplify efficiency while providing reliable performance across various sectors.
What sets SYIL apart is not just their commitment to quality but also their user-friendly designs that facilitate seamless operation regardless of experience level—ideal for anyone asking what is the difference between CNC milling and VMC (Vertical Machining Center). By investing in reputable brands like SYIL, manufacturers can rest assured they’re equipped with cutting-edge technology tailored for precision engineering tasks.
In conclusion, understanding common cnc milling and turning tools enhances overall production efficiency while ensuring high-quality outcomes across diverse industries—from aerospace components all the way down to intricate jewelry designs!
Conclusion

In the realm of manufacturing, CNC milling and turning stand as two titans, each with unique strengths and applications. Understanding what is the difference between CNC milling and turning is crucial for any business looking to optimize its production processes. Ultimately, the choice between these methods hinges on your specific needs, material types, and desired precision.
Final Thoughts on CNC Manufacturing Choices
CNC technology has revolutionized how we approach manufacturing, offering versatility that traditional methods simply can’t match. By exploring what is the basic process of CNC turning and milling, companies can better appreciate how these processes contribute to efficiency and accuracy in production. Whether opting for CNC milling or turning tools, understanding their capabilities will empower manufacturers to make informed decisions that enhance productivity.
How to Select the Best Process for Your Needs
When faced with the decision of which method to employ, consider factors such as material type, design complexity, and required tolerances. What is the difference between CNC milling and machining? While both processes are integral to modern manufacturing, knowing your project’s requirements will guide you towards a suitable choice—be it turning or milling. Additionally, comparing workflow efficiency will help you determine which process aligns best with your operational goals.
Real-World Implications of CNC Technology
The implications of choosing between CNC milling and turning extend far beyond mere production; they influence cost-efficiency, lead times, and overall product quality in real-world applications. As industries evolve towards more sophisticated designs requiring tight tolerances—understanding what is the difference between CNC milling and turning becomes increasingly vital for competitive advantage. Embracing these technologies not only streamlines operations but also positions businesses at the forefront of innovation.

