Introduction

In the world of CNC machining, the choice of materials is paramount to achieving precision and efficiency. CNC machining materials encompass a wide range of options, each with unique properties that influence the final product's quality and performance. Understanding these materials is not just a technical necessity; it’s crucial for anyone looking to optimize their machining processes.
Understanding CNC Machining Materials
CNC machining relies on various materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and composites. Each type of material brings its own set of advantages and challenges to the table. Knowing what material is used for CNC machining can make all the difference in ensuring that your project meets its specifications and expectations.
Importance of Material Selection
Selecting the right material is critical because it directly impacts factors such as durability, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturability. This process involves considering not only the mechanical properties but also how these materials interact with different CNC machines and tools. For instance, understanding what materials cannot be CNC machined helps avoid costly mistakes during production.
Common CNC Machining Applications
CNC machining finds applications across numerous industries—from aerospace to automotive—where precision is non-negotiable. The versatility of metal CNC machining materials makes them particularly popular for components requiring strength and stability under stress. Additionally, knowing how to select the right materials for CNC machining can lead to innovative solutions in product design and manufacturing efficiency.
Overview of CNC Machining Materials

Understanding the landscape of CNC machining materials is crucial for anyone involved in manufacturing or design. With a plethora of options available, knowing what material is used for CNC machining can make or break your project. From metals to plastics, each type offers unique properties that cater to specific applications.
Types of CNC Machining Materials
CNC machining materials can be broadly categorized into three main types: metals, plastics, and wood. Metals such as aluminum, steel, and titanium dominate the industry due to their strength and durability; these are often referred to as metal CNC machining materials. Plastics like acrylic and nylon provide lightweight alternatives with good machinability, while wood offers a natural aesthetic for various applications.
When considering what materials cannot be CNC machined, it's essential to note that certain composites and ceramics may pose challenges due to their hardness or brittleness. Additionally, some soft or flexible materials might not hold up under the precise conditions required for effective machining. Understanding these categories helps streamline the selection process when examining a CNC machining materials list.
Key Properties of Popular Materials
The key properties of popular CNC machining materials vary significantly based on their type—metals generally exhibit high tensile strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for structural components. On the other hand, plastics are known for their versatility and ease of processing but may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals do. Wood brings its own set of qualities such as aesthetic appeal and workability but can also be susceptible to moisture changes.
When selecting the right materials for CNC machining projects, it’s vital to consider factors like weight-to-strength ratio and thermal expansion characteristics. These properties directly influence not only the performance but also the longevity of the finished product in real-world applications. Thus, understanding these key attributes will help you make informed choices during material selection.
How Material Affects Machining Processes
The choice of material significantly impacts various aspects of CNC machining processes including tool selection, speed settings, and cutting techniques employed during production. For instance, harder metals require specialized tooling made from more durable substances like carbide to maintain efficiency without excessive wear on tools—this is critical when working with metal CNC machining materials where precision is paramount. Conversely, softer plastics can often be machined at higher speeds with standard tooling due to their forgiving nature.
Additionally, how do you select the right materials for CNC machining? Consider factors such as desired strength requirements and environmental conditions where the final product will be used; this assessment will guide you toward optimal material choices that align with your project goals. Ultimately, understanding how each material affects these processes ensures smoother operations while enhancing overall productivity in any manufacturing setting.
Metals: The Backbone of CNC Machining

Metals are undeniably the backbone of CNC machining, providing strength, durability, and precision that many applications demand. When considering CNC machining materials, metals often come to mind first due to their versatility and widespread availability. Understanding which metal CNC machining materials are best suited for specific tasks is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Common Metal CNC Machining Materials
Among the most common metal CNC machining materials are aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and excellent machinability, making it ideal for a range of applications from automotive components to aerospace parts. Steel offers strength and durability but may require special tools due to its toughness; meanwhile, brass is often used in electrical components due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Using Metal
One significant advantage of using metal in CNC machining is its superior mechanical properties compared to other materials like plastics or wood. Metals can withstand extreme temperatures and stress without deforming, which makes them perfect for high-performance applications. Additionally, the range of finishes available with metal allows for enhanced aesthetic appeal while maintaining functionality—definitely a win-win situation!
Limitations and Challenges
For instance, metals can be more expensive than other options such as plastics or wood; thus budget-conscious projects might shy away from them. Furthermore, certain metals may pose challenges during the cutting process—like excessive heat generation—which could lead to tool wear or even damage if not managed properly.
Plastics in CNC Machining
In the realm of CNC machining materials, plastics have carved out a significant niche. They offer unique properties that make them suitable for various applications, from prototypes to functional components. Understanding the benefits and limitations of plastic materials can help you make informed decisions when selecting materials for your CNC projects.
Benefits of Plastic Materials
One of the standout benefits of plastic materials in CNC machining is their lightweight nature. This characteristic not only makes them easier to handle but also reduces shipping costs and improves energy efficiency during production. Additionally, plastics can be engineered to exhibit excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for applications where exposure to harsh substances is a concern.
Another advantage is their versatility; plastics can be formulated to meet specific requirements such as flexibility, rigidity, or impact resistance. This adaptability allows designers and engineers to create parts that are tailored precisely to their needs without compromising on performance. Furthermore, plastic machining often results in lower tooling costs compared to metal cnc machining materials, which can be a game-changer for budget-conscious projects.
Finally, the aesthetic appeal of plastics cannot be overlooked; they can easily be colored or finished to enhance visual quality. This makes them particularly attractive for consumer products where appearance matters just as much as functionality. With all these benefits combined, it’s clear why many industries are turning toward plastic materials in their CNC processes.
Most Suitable Plastics for CNC Machining
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is one popular choice; it offers high impact resistance and good dimensional stability while being relatively easy to machine. Another excellent option is Polycarbonate (PC), known for its toughness and transparency—perfect for applications requiring visibility.
Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP) are also frequently used due to their chemical resistance and low friction properties; these qualities make them suitable for parts like gears or containers that may come into contact with various substances. For more specialized applications, Nylon (PA) is often preferred because of its strength and wear resistance—ideal when durability is paramount in your design considerations.
Lastly, don’t forget about Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), commonly known as acrylic; it provides an attractive finish with high clarity while being relatively easy to machine compared to other plastics on the market. When constructing your cnc machining materials list, keep these options in mind—they could save you time and headaches down the line!
When to Avoid Plastic Materials
While plastics have numerous advantages in CNC machining applications, there are times when they simply aren’t the best choice—especially when considering what materials cannot be CNC machined effectively. For instance, if your project requires high-temperature tolerance or structural integrity under heavy loads, metals may outperform plastics significantly in those scenarios.
Additionally, some environments expose parts made from certain plastics to chemicals or UV radiation that could degrade them over time—making metals or composites more suitable alternatives here too! If precision tolerances are critical—for example in aerospace components—you might find that metal cnc machining materials provide superior accuracy compared with most plastic options available today.
In summary, although plastic offers many benefits within the world of cnc machining materials—from cost-effectiveness through aesthetic appeal—it’s essential always evaluate whether they fit your specific application needs before diving headfirst into production!
Wood and Its Applications

Popular Wood Types for CNC Machining
Several types of wood are commonly used in CNC machining due to their workability and finish quality. Hardwoods like oak, maple, and cherry are often chosen for their durability and rich grain patterns, making them ideal for high-quality furniture and decorative items. On the other hand, softwoods such as pine or cedar are frequently selected for projects requiring lighter weight or cost-effective solutions.
In addition to these traditional choices, engineered woods like plywood and MDF (medium-density fiberboard) have gained popularity in CNC applications due to their stability and uniformity. These materials allow for more intricate designs without the risk of warping or splitting that natural woods might present. When considering what material is used for CNC machining, it’s essential to evaluate both the aesthetic qualities and functional requirements of your project.
Techniques for Machining Wood
Machining wood with a CNC machine requires specific techniques tailored to its unique properties. Utilizing sharp tools designed specifically for wood can significantly improve cut quality while minimizing splintering—an issue that can plague less careful setups. Adjusting feed rates and spindle speeds is also crucial; too fast can lead to burning the wood, while too slow may cause tear-out along the grain.
Additionally, employing proper fixturing techniques ensures that your workpiece remains stable during machining operations. This stability is vital when performing detailed cuts or engravings that require precision—after all, no one wants their masterpiece ruined by an unexpected slip! Understanding how do you select the right materials for CNC machining will help you choose appropriate woods based on your project needs.
Considerations for Wood Machining
When working with wood as a CNC machining material, several considerations must be taken into account to ensure success. First off is moisture content; high humidity levels can cause wooden pieces to expand or contract unpredictably during processing which could alter dimensions or even ruin parts entirely! Therefore, selecting properly dried lumber is paramount in avoiding issues later on.
Another important aspect involves understanding what materials cannot be CNC machined effectively; some woods may contain knots or defects that complicate cutting processes—these should be avoided if possible! Finally, always consult a comprehensive cnc machining materials list before starting your project; this will help you identify suitable types of wood along with any necessary tooling adjustments required during production.
Special Materials: Composites and Alloys
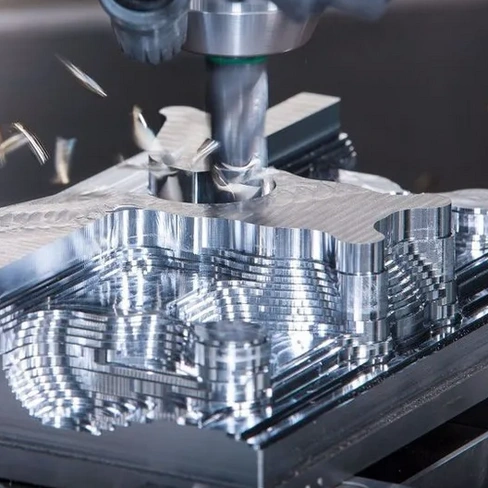

When it comes to CNC machining materials, not all substances are created equal. While metals, plastics, and wood dominate the landscape, there are also composites and alloys that can offer unique benefits. However, it's essential to understand what materials cannot be CNC machined before diving into these specialized options.
What Materials Cannot Be CNC Machined?
While CNC machining is incredibly versatile, certain materials pose significant challenges or are simply unsuitable for this process. For instance, brittle materials like glass or ceramics often shatter under the stress of machining operations. Additionally, extremely hard substances such as diamond require specialized tools that go beyond traditional CNC capabilities; thus they are typically excluded from the standard CNC machining materials list.
Another category to consider is soft or elastic materials like rubber or certain foams; these can deform during machining and yield unsatisfactory results. Lastly, some composite materials with a high fiber content may cause excessive wear on cutting tools or may not hold dimensional stability during the process. Understanding what materials cannot be CNC machined is crucial for effective project planning.
Overview of Composites in CNC
Composites have emerged as a game-changer in the world of CNC machining materials due to their unique properties and lightweight nature. These engineered combinations of two or more constituent materials offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios while maintaining flexibility and resistance to corrosion. Common types include carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRP) and glass fiber-reinforced polymers (GFRP), both of which can be tailored for specific applications.
One key advantage of using composites in CNC machining is their ability to withstand harsh environments without compromising structural integrity. This makes them popular in industries ranging from aerospace to automotive manufacturing where performance is paramount. However, selecting the right composite material requires careful consideration; understanding how different composites interact with standard machining processes will help ensure optimal results.
Alloys: The Versatile Alternative
Alloys represent another fascinating category within cnc machining materials that provides versatility across various applications. By combining different metals—such as aluminum with copper or nickel with titanium—manufacturers create alloys that enhance desirable properties like strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion while minimizing weaknesses found in pure metals alone.
Metal cnc machining materials often include popular alloys like aluminum 6061 for its excellent machinability and steel alloys known for their durability under stress loads. The incorporation of alloying elements allows manufacturers not only to meet specific mechanical requirements but also to achieve cost-effectiveness by optimizing material usage based on project needs. As you explore your options for selecting the right materials for CNC machining projects, don't overlook the potential advantages offered by both composites and alloys—they might just be your best bet!
Selecting the Right Materials

Choosing the right materials for CNC machining is akin to picking the perfect ingredients for a gourmet meal; it can make or break your project. The selection process involves balancing various factors such as material properties, machining capabilities, and application requirements. Understanding these aspects ensures that you achieve optimal results while avoiding costly mistakes.
Factors to Consider for Material Selection
When selecting CNC machining materials, several critical factors come into play. First, consider the mechanical properties of the material, such as strength, hardness, and ductility—these will influence how well the material can withstand operational stresses. Additionally, think about machinability; some materials are easier to cut and shape than others, which affects production time and tool wear.
Another essential factor is thermal conductivity; materials with high thermal conductivity may require special cooling techniques during machining to prevent overheating. Also, keep in mind the intended application of the final product—certain environments may demand specific material characteristics like corrosion resistance or lightweight properties. Ultimately, understanding what materials cannot be CNC machined will save you time and resources by steering you away from unsuitable choices.
Understanding the CNC Machining Materials List
A comprehensive CNC machining materials list includes a variety of options ranging from metals to plastics and composites. Metals like aluminum and steel are often favored due to their durability and versatility in applications requiring strength—these are prime examples of metal CNC machining materials that serve various industries effectively. On the other hand, plastics like acrylic or nylon offer unique benefits in applications requiring lightweight components or chemical resistance.
In addition to traditional options, composites have emerged as strong contenders in advanced manufacturing scenarios due to their enhanced properties like high strength-to-weight ratios. When reviewing your CNC machining materials list, it’s crucial to match each potential material with your project's specific needs while considering any limitations they might present during processing—after all, not all candidates will fit seamlessly into your workflow.
Tips for Beginners
For those new to CNC machining, navigating through various material options can feel overwhelming at first—but fear not! Start by familiarizing yourself with common metal CNC machining materials such as aluminum alloys or stainless steel since they offer a great balance between ease of use and performance for beginners. As you gain confidence in your skills and understanding of what material is used for CNC machining tasks, gradually explore plastics or even wood depending on your project requirements.
Don’t hesitate to consult experienced machinists or online forums when you're unsure about selecting appropriate raw materials for machining; sharing knowledge can significantly shorten your learning curve! Lastly, always remember that trial and error is part of mastering this craft—so take notes on what works best for you while keeping an eye out for what materials cannot be CNC machined effectively.
Conclusion

In the world of CNC machining, mastering material choices is crucial for achieving optimal results. Understanding the various CNC machining materials available can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of your projects. Whether you're working with metals, plastics, or wood, selecting the right material can make all the difference in your machining process.
Mastering Material Choices for CNC Machining
To truly excel in CNC machining, it's essential to know what materials work best for your specific applications. The question What material is used for CNC machining? often leads to a myriad of answers—each suited to different needs and outcomes. By familiarizing yourself with a comprehensive CNC machining materials list, you can ensure that you’re making informed decisions that align with your project goals.
Additionally, understanding which materials cannot be CNC machined is equally important; some substances simply don't lend themselves well to this method due to their physical properties or composition. For instance, certain soft foams or highly brittle ceramics may pose challenges during the machining process. By mastering these nuances in material selection, you're setting yourself up for success in every project.
The Future of CNC Machining Materials
Looking ahead, the future of CNC machining materials appears promising as advancements continue to emerge in both technology and material science. New composites and alloys are being developed that could revolutionize how we approach manufacturing processes—offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved machinability compared to traditional options like metal CNC machining materials. With ongoing research into sustainable alternatives and innovative solutions, we may soon see an expanded palette of options available for machinists.
Moreover, as industries evolve and demand increases for specialized components, understanding how to integrate new materials into existing workflows will be vital. This adaptability will not only keep businesses competitive but also drive innovation across various sectors relying on precision engineering techniques like CNC machining.
Final Thoughts on Material Selection Strategies
When it comes down to it, selecting the right materials for CNC machining isn’t just about picking what's popular or readily available; it's about aligning your choices with project specifications and desired outcomes. Factors such as cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of processing should guide your decision-making process while considering what are the raw materials for machining in each scenario.
Remember that knowledge is power: equip yourself with insights about metal types used in projects while also exploring alternative options like plastics or wood when appropriate. With a strategic approach towards material selection strategies combined with an understanding of what works best under specific conditions, you’ll be well on your way toward mastering the art of CNC machining.

