Introduction

In the world of electronics, precision is paramount, and that's where PCB mills come into play. These machines are designed to create printed circuit boards (PCBs) with remarkable accuracy, enabling engineers and hobbyists alike to bring their electronic designs to life. But before you dive into the intricate world of PCB milling, it’s essential to grasp what it entails and how it differs from other methods like routing.
Understanding PCB Mills and Their Functionality
A PCB mill is a specialized machine that uses cutting tools to remove material from a substrate, shaping it into a functional circuit board. The functionality of these mills goes beyond mere cutting; they can drill holes, carve out traces, and even create complex geometries that traditional methods struggle with. Understanding how these machines operate is crucial for anyone looking to produce high-quality PCBs efficiently.
The Importance of Choosing the Right PCB Mill
Selecting the right PCB mill can make or break your project—literally! With various models available on the market, understanding the specifications that matter most for your needs will ensure you achieve optimal results in your milling of printed circuit boards. Factors such as precision, speed, and ease of use should guide your decision-making process.
Getting Started with PCB Milling Basics
Before embarking on your journey into the realm of PCB milling, it's beneficial to familiarize yourself with some basic concepts. You'll want to explore key terms like What is PCB milling? which encompasses various techniques used in this field. Additionally, understanding What are the advantages of PCB milling? will help you appreciate why this method has gained popularity among professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike.
What is PCB Milling?
PCB milling is a process that involves the mechanical removal of material from a printed circuit board (PCB) to create specific patterns and features. This technique allows for the precise shaping of copper layers, resulting in high-quality circuit boards ready for electronic components. Unlike traditional etching methods, which rely on chemical processes, milling provides an efficient and accurate way to produce PCBs.
Overview of PCB Milling Techniques
When we talk about PCB milling techniques, we’re diving into a world of precision engineering. The most common methods include CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling and manual milling, each with its own set of advantages. CNC milling is particularly popular due to its automation capabilities, allowing for intricate designs and repeatability that manual methods struggle to achieve.
In addition to CNC and manual techniques, there are specialized tools like engraving machines that can also be used for PCB fabrication. These machines excel in creating detailed features such as vias and traces with minimal waste material. Ultimately, understanding these various techniques helps you determine the best approach for your specific project needs.
Key Components of a PCB Mill
A typical PCB mill consists of several key components that work together to ensure successful milling operations. At the heart of it all is the spindle or cutting head, which houses the cutting tools responsible for removing material from the board's surface. Other essential components include a robust frame for stability, motorized axes for movement control, and software that translates design files into machine instructions.
Moreover, dust extraction systems are crucial in maintaining a clean working environment by removing debris generated during the milling process. These systems not only enhance visibility but also prolong the life of your equipment by preventing dust buildup on sensitive parts. Together, these components make up an efficient PCB fabrication machine capable of producing high-quality results.
Real-World Applications of PCB Milling
The applications of PCB milling are vast and varied across multiple industries ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace engineering. In prototyping environments, engineers often use PCB mills to quickly create custom circuit boards tailored to their specifications without waiting weeks for outsourced production. This rapid turnaround time fosters innovation by allowing designers to test ideas more freely.
Additionally, small-batch production runs benefit greatly from this technology as it eliminates setup costs associated with larger manufacturing processes like etching or stamping. Industries such as telecommunications utilize PCB milling techniques to produce complex circuit boards essential for modern communication devices like smartphones and routers. Overall, whether it's rapid prototyping or small-scale production runs, the versatility of pcb mills makes them indispensable in today’s tech landscape.
What is the Difference Between Milling and Routing PCB?
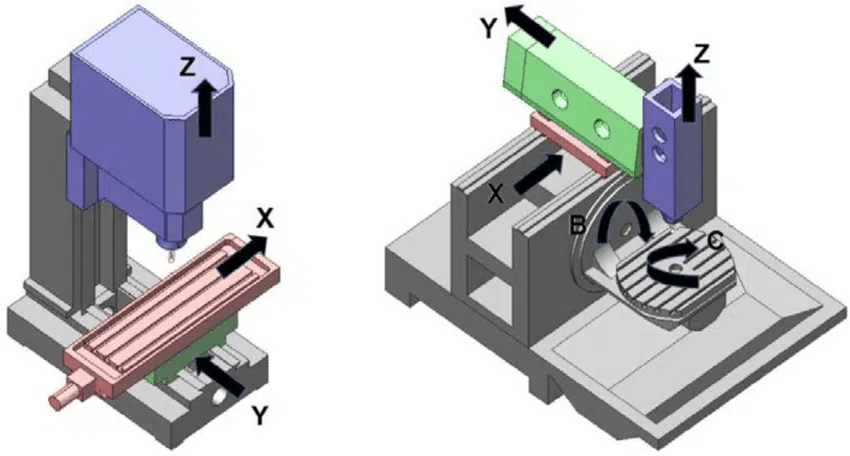
Defining Milling and Routing Processes
Milling of printed circuit boards involves removing material from a solid substrate to create intricate designs, tracks, and pads essential for electrical connectivity. This process uses a rotating cutting tool that precisely carves out patterns according to a digital design file. On the other hand, routing typically refers to the method of cutting out entire shapes or profiles from larger board materials, often used when creating outlines or separating multiple boards from a single sheet.
In essence, while both milling and routing involve subtractive processes, milling focuses on detailed internal features like traces and holes, whereas routing deals with external contours of the PCBs. The choice between these methods can significantly impact your project’s final outcome. So when you ask yourself, What is PCB milling? remember it's all about precision in crafting those tiny details.
Pros and Cons of Each Method
Milling offers several advantages that make it a go-to choice for many PCB designers: high precision in creating complex geometries and the ability to work with various materials without needing extensive setup changes. However, it can be slower than routing due to its intricate nature—perfect for small batches or prototypes but perhaps not ideal for mass production.
Routing shines in speed; it's excellent for quickly producing simple shapes or outlines at scale. Yet this method may compromise some detail compared to milling; fine features might not be as well-defined when using routers alone. When weighing What are the advantages of PCB milling? against routing's benefits, consider your project's specific requirements—precision versus speed might just tip the scales one way or another.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Deciding whether to use milling or routing boils down to your project’s needs—think about factors like complexity, volume, and budget constraints. If you're working on prototype circuits where intricate details matter most, opting for a PCB mill will likely yield superior results due to its precision capabilities. Conversely, if you're ramping up production with simpler designs that require quick turnaround times, routing could be your best bet.
Ultimately, understanding What is the difference between milling and routing PCB? helps you align your choice with project goals effectively. Don’t forget that advancements in technology also mean new hybrid machines are emerging—some capable of both processes! So stay informed about innovations in PCB fabrication machine options that might offer you flexibility as you navigate your design journey.
What are the Advantages of PCB Milling?

Precision and Accuracy in PCB Production
One of the most significant advantages of using a pcb mill is the level of precision it offers during the milling of printed circuit boards. Unlike traditional methods, which may introduce errors due to chemical processes, PCB milling utilizes cutting tools that ensure each trace and pad is accurately formed according to design specifications. This high degree of accuracy not only enhances functionality but also minimizes potential errors in electronic circuits.
Moreover, when discussing what is PCB milling?, it's essential to highlight that this process allows for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve with other techniques. The precision involved in PCB milling means that even complex layouts can be executed flawlessly, ensuring reliability in performance. Ultimately, this level of detail contributes significantly to the overall quality and longevity of the final product.
Cost-Effectiveness in Small Batch Manufacturing
Another compelling reason why many turn to PCB milling is its cost-effectiveness, particularly for small batch manufacturing runs. Traditional methods often require expensive setups and tooling changes for different designs; however, a pcb mill can quickly switch between projects without incurring substantial costs or extended downtime. This flexibility enables manufacturers to produce low volumes economically while maintaining high-quality standards.
In addition, when considering what is the difference between milling and routing PCB? It’s clear that milling is better suited for rapid prototyping or custom board production where costs need to be kept low without sacrificing quality. By eliminating unnecessary waste and reducing material costs through precise cuts, businesses can optimize their budgets effectively while still producing top-notch PCBs.
The Flexibility of PCB Milling
Flexibility is another standout advantage offered by pcb mills in comparison with other fabrication methods like etching or routing techniques. With advanced software integration and user-friendly interfaces, operators can easily modify designs on-the-fly based on project requirements or client feedback—something that's not as seamless with traditional methods. This adaptability makes it an ideal choice for both hobbyists working on personal projects and professionals tackling diverse client demands.
Furthermore, understanding what is a PCB fabrication machine highlights how modern machines incorporate multi-functional capabilities—allowing users not only to mill but also drill holes or engrave components—all from one device! Such versatility means you can explore various applications within electronics without needing multiple machines cluttering your workspace. In essence, this flexibility empowers users by providing them with more creative freedom while simplifying their workflow.
Exploring PCB Fabrication Machines

Essential Features of PCB Fabrication Machines
A high-quality PCB fabrication machine should have several essential features that cater to both novice and experienced users alike. First and foremost, precision is key; a good machine must be able to achieve tight tolerances during the milling process to ensure functionality and reliability in your designs. Additionally, user-friendly software integration can greatly enhance workflow efficiency by allowing seamless design uploads and modifications.
Another important feature is versatility; an ideal PCB mill should be capable of handling different materials such as FR-4, aluminum, or even flexible substrates. This flexibility opens up possibilities for various applications beyond just traditional PCBs. Finally, robust support and service options from manufacturers can provide peace of mind when investing in a new piece of equipment.
Popular Brands in PCB Fabrication
In the realm of PCB fabrication machines, several brands have established themselves as leaders through innovation and quality. Brands like LPKF, Bantam Tools, and T-Tech are well-known for their reliable machinery that caters to diverse needs within the industry. Each brand offers unique features tailored towards specific aspects of the PCB milling process.
LPKF stands out with its advanced laser technology while Bantam Tools focuses on user-friendly desktop solutions suitable for hobbyists and small businesses alike. T-Tech has built a reputation on producing robust systems ideal for high-volume production runs as well as prototyping needs. Choosing between these brands often comes down to specific project requirements and budget considerations.
SYIL CNC Machine: A Top Choice
Among these popular brands lies SYIL CNC machines, which have garnered attention as a top choice for many professionals engaged in PCB milling processes. What sets SYIL apart is its commitment to delivering high-performance CNC machines that combine affordability with cutting-edge technology—perfectly suited for both small-scale operations and larger manufacturing setups alike.
The SYIL CNC machine boasts impressive capabilities such as multi-axis machining which enhances its versatility across various projects including intricate designs where precision matters most. Additionally, users appreciate its straightforward setup process paired with comprehensive software support that simplifies everything from design input to final output—a win-win situation!
Investing in a SYIL CNC machine means you’re not just getting any ordinary pcb mill; you’re equipping yourself with an efficient tool that streamlines your entire workflow while ensuring accuracy at every turn.
The PCB Milling Process Explained
PCB milling is an innovative technique that transforms raw materials into functional circuit boards with precision and efficiency. This section will walk you through the PCB milling process, offering a detailed step-by-step guide, practical tips for setting up your PCB mill, and insights into common challenges faced during the milling of printed circuit boards. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, understanding these elements can enhance your PCB fabrication experience.
Step-by-Step Guide to PCB Milling
The first step in the PCB milling process is to prepare your design files, typically in Gerber format, which contain all necessary information for routing and cutting. Next, you'll need to set up your PCB mill by securing the material onto the machine's bed and ensuring that the milling bit is appropriately calibrated for depth and speed. Once everything is set up correctly, you can initiate the milling operation; this involves removing excess material from the board to create traces and pads according to your design.
After completing the initial milling process, it’s essential to inspect the board for any defects or inaccuracies—this ensures high-quality results that meet your project's specifications. If everything looks good, proceed with additional operations like drilling holes or applying surface finishes if required. Finally, clean up any debris from the milling process before moving on to assembly or further testing of your newly created printed circuit board.
Tips for Setting Up Your PCB Mill
Setting up a PCB mill can be straightforward if you follow some best practices. First off, always ensure that you use high-quality materials suitable for your project; this will directly impact both performance and durability of your final product. Additionally, calibrate your machine regularly—this means checking alignment and ensuring that tools are sharp—to maintain precision during each job.
Don't forget about software settings! Make sure you're using compatible software that can effectively translate your design files into commands understood by your pcb mill; this includes selecting appropriate feed rates and spindle speeds based on material type. Lastly, keep safety in mind: wear protective gear such as goggles while operating machinery to safeguard against debris or unexpected mishaps during the milling of printed circuit boards.
Common Challenges and Solutions in PCB Milling
While pcb milling offers numerous advantages over traditional methods like etching, it does come with its own set of challenges. One common issue is tool wear; as bits become dull over time from repeated use, they can lead to imprecise cuts or even damage materials being milled. To combat this problem, schedule regular maintenance checks on tools and replace them as needed—keeping an eye on performance will save you headaches down the road.
Another challenge might be achieving consistent depth across all areas of a board; variations in material thickness can affect results significantly during production runs. To address this issue effectively, invest time in properly leveling both workpieces and machinery prior to starting jobs—it’s worth it when aiming for uniformity! Lastly, if you're experiencing issues with excessive vibration during operation—which could lead not only to poor quality but also potential damage—consider stabilizing your setup by adding weight or using vibration-dampening mounts.
PCB Milling vs Etching

Understanding Etching in PCB Production
Etching is a widely used technique in PCB production that involves removing unwanted copper from a substrate to create conductive pathways. Typically, this process starts with applying a photoresist layer to the copper-clad board, which is then exposed to UV light through a mask. The exposed areas are developed and subsequently etched away using chemical solutions, leaving behind the desired circuitry pattern.
The etching process can be highly efficient for mass production since it allows for intricate designs to be created quickly and uniformly across multiple boards. However, it does have its limitations; for instance, fine details may not always be captured accurately depending on the quality of the mask and exposure process. Additionally, etching can produce hazardous waste that requires careful disposal, making environmental considerations an important factor in its use.
Comparing Efficiency and Results of Both Methods
When comparing efficiency between milling of printed circuit boards and etching, each method has its strengths depending on the specific project requirements. Milling typically offers more precision when creating complex geometries or fine features because it mechanically removes material rather than relying on chemical reactions like etching does. This means that PCB milling can achieve tighter tolerances and finer details without worrying about undercutting or other issues associated with chemical processes.
However, while PCB milling may excel in precision for small batches or prototypes—thanks to its ability to quickly adjust designs—it may not always be as cost-effective as etching for larger runs where economies of scale come into play. In terms of results, both methods can produce high-quality PCBs but may differ significantly in finish; milled boards often exhibit a more rugged appearance compared to the smooth finish achieved through etching processes.
When to Opt for Milling Over Etching
Choosing between milling and etching largely depends on your specific project needs—especially regarding scale, complexity, and budget constraints. If you’re working on low-volume production runs or need rapid prototyping capabilities with quick design revisions, opting for a pcb mill would likely serve you better due to its flexibility and speed in adjusting designs without extensive setup changes.
On the other hand, if your project demands high volumes with less intricate designs where uniformity is key—like basic circuit layouts—etching could be the way forward due to its cost-effectiveness at scale. Ultimately, understanding what you need from your PCB fabrication machine will help guide your decision-making process when weighing these two popular methods against each other.
Conclusion

In the world of electronics, the choice of a PCB mill can significantly influence your project's success. Understanding what PCB milling is and how it differs from routing will help you select the right technique for your needs. With the advantages of precision and flexibility, PCB milling stands out as a compelling option for many manufacturers.
Key Takeaways for Choosing Your PCB Mill
When selecting a PCB mill, consider factors such as precision, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. The milling process offers distinct advantages, especially in small batch manufacturing where customization is key. Additionally, understanding what is PCB fabrication machine can guide you toward making informed decisions that align with your production goals.
The Future of PCB Milling Technology
The future of PCB milling technology looks promising as advancements continue to emerge in automation and software integration. Innovations may lead to even greater efficiency in the PCB milling process while reducing costs and enhancing capabilities. As industries increasingly adopt this technology, we can expect improved applications across various sectors that rely on printed circuit boards.
Final Thoughts on PCB Manufacturing Choices
Ultimately, choosing between methods like milling vs etching hinges on your specific project requirements and desired outcomes. Each method has its unique advantages; however, understanding what are the advantages of PCB milling will often sway decisions toward this technique for its precision and adaptability. In a rapidly evolving field like electronics manufacturing, staying informed about all available options is crucial for success.

