Introduction

In the world of manufacturing, CNC milling operations stand out as a cornerstone of precision engineering. Understanding CNC milling operations is essential for anyone looking to delve into the realm of modern machining. This technology not only enhances efficiency but also ensures that components are crafted with remarkable accuracy, making it a go-to method for producing intricate designs.
Understanding CNC Milling Operations
So, what is the process of CNC milling? At its core, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling involves the use of computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece, shaping it into the desired form. The question Is CNC machining milling? often arises; while they are related, not all CNC machining processes involve milling—some may focus on turning or other techniques.
When exploring how CNC milling works in practice, one can appreciate its versatility and adaptability across various materials and applications. From aluminum to plastics, this method allows for a wide range of products to be manufactured with consistent quality and repeatability. The basic CNC milling operation typically involves loading a design file into the machine's software, setting up tooling and fixtures, and letting the machine do its magic.
The Importance of Precision in Machining
Precision is paramount in any machining process; however, it takes on an even greater significance in CNC milling operations where tolerances can be measured in microns. A slight error can lead to significant issues down the line—whether it's wasted materials or malfunctioning parts—so understanding how precision impacts outcomes is critical for success in this field. This emphasis on accuracy leads many aspiring machinists to wonder: what is a CNC mill machinist?
A skilled CNC mill machinist must possess an eye for detail and an understanding of complex machinery to ensure that each component meets exact specifications. They play a vital role in maintaining quality control throughout production processes while also adapting quickly to changes in design or material requirements. Ultimately, their expertise contributes significantly to achieving high-quality results consistently.
Key Components of CNC Milling
To fully grasp how CNC milling works effectively, one must familiarize themselves with its key components. These include everything from the machine itself—often referred to as a CNC mill—to various tooling options that allow for different cutting techniques and finishes. Additionally, software plays an essential role by translating design files into commands that guide the machine’s movements during operation.
Understanding these components provides insight into what makes up an efficient workflow within any given facility utilizing cnc milling operations. From selecting appropriate tools based on material type to programming specific cutting paths via software interfaces—the interplay between these elements determines overall productivity and output quality within manufacturing environments.
CNC Milling Operation Overview
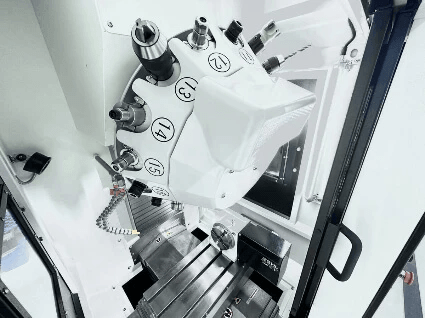
CNC milling operations have revolutionized the manufacturing landscape, allowing for precision and efficiency that manual machining simply can't match. At its core, CNC milling involves using computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece, transforming it into a desired shape or size. This process is crucial in various industries, from aerospace to automotive, where accuracy is non-negotiable.
What is the process of CNC milling?
So, what is the process of CNC milling? It begins with a digital design created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, which serves as the blueprint for the final product. Once this design is ready, it's translated into G-code—a language that tells the machine how to move and operate—enabling precise cutting and shaping of materials like metal or plastic.
During a typical CNC milling operation, the workpiece is securely fastened to the machine bed while rotating cutting tools carve away excess material according to programmed specifications. This method not only enhances productivity but also ensures repeatability; each part can be manufactured identically without deviation. Ultimately, understanding this process helps demystify how complex parts are produced with such remarkable accuracy.
Is CNC machining milling or something else?
Now you might be wondering: Is CNC machining milling or something else? The answer lies in understanding that while all CNC milling operations are a form of CNC machining, not all CNC machining involves milling processes. In fact, CNC encompasses various techniques including turning and electrical discharge machining (EDM), each serving different purposes depending on project requirements.
CNC milling specifically refers to processes involving rotating cutters that remove material from stationary workpieces—think of it as sculpting with machinery! On the other hand, turning involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutter to achieve desired shapes. So when considering your options in manufacturing processes, it’s essential to identify whether you need a basic CNC milling operation or another type of CNC technique altogether.
How CNC milling works in practice
How does all this theory translate into real-world applications? Well, how CNC milling works in practice combines technology with skilled craftsmanship—enter the role of a CNC mill machinist! These professionals are responsible for setting up machines based on blueprints and adjusting parameters like speed and feed rates to ensure optimal performance during production runs.
In practical terms, once everything's set up correctly—tools attached and programs loaded—the machinist monitors operations closely while making adjustments as necessary throughout the run. This hands-on approach ensures quality control at every stage; if anything seems off during production (like an unexpected noise), they can troubleshoot immediately before issues escalate. Thus, mastering both technical knowledge and practical skills makes for successful execution within any basic CNC milling operation!
Essential CNC Milling Machine Components

CNC milling operations rely on a variety of components that work together to create precise and intricate parts. Understanding these essential components is key to appreciating how CNC milling works and the overall efficiency of the process. From the machine itself to tooling and software, each element plays a vital role in achieving high-quality results.
Overview of the SYIL CNC machine
The SYIL CNC machine stands out in the world of CNC milling operations for its impressive versatility and reliability. Designed for both hobbyists and professionals, this machine offers various configurations that cater to different machining needs. With features like high-speed spindles and robust construction, it allows machinists to effectively execute what is the basic CNC milling operation while ensuring accuracy.
Understanding tooling and attachments
Tooling is at the heart of every successful CNC milling operation; without the right tools, even the most advanced machinery will fall short. Various types of cutting tools—such as end mills, drills, and reamers—are specifically designed for different tasks within what is the process of CNC milling? Attachments like tool holders play an equally critical role by securing these tools in place during operation.
Moreover, choosing appropriate tooling not only affects precision but also influences factors like cutting speed and feed rate—a topic we’ll dive into later on! Each tool has its unique geometry tailored for specific materials and applications; understanding this can significantly enhance a machinist's ability to execute complex designs efficiently. So when pondering What is a CNC mill machinist?, remember that their expertise extends beyond just operating machinery—it encompasses selecting suitable tools as well.
The role of software in CNC milling operations
Software serves as the brain behind any effective CNC milling operation; it converts designs into actionable commands that guide machines through intricate movements. Programs such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) allow users to create detailed models before transitioning them into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems for actual production processes—this synergy between design software ensures what is the basic CNC milling operation runs smoothly from concept to creation.
In addition, modern software solutions often come equipped with simulation features that enable machinists to visualize potential outcomes before committing resources—a real game-changer! These simulations help identify any issues early on in what could otherwise be costly mistakes during physical machining processes. As you can see, having an adept understanding of software applications significantly enhances how effectively one can manage their role as a machinist.
Factors Influencing CNC Milling Accuracy

Importance of Material Selection
Choosing the right material is crucial in any CNC milling operation. Different materials react uniquely to machining processes; some may warp or chip easily while others can withstand higher cutting speeds without losing integrity. When considering what is the basic CNC milling operation, it's clear that selecting a compatible material enhances both efficiency and accuracy in machining.
Moreover, different materials have varying densities and hardness levels which can significantly affect tool wear and lifespan. For instance, aluminum is easier to machine compared to stainless steel but may require different tooling strategies to achieve optimal results. Ultimately, understanding how material properties influence CNC machining milling processes will lead to better outcomes in precision engineering.
Influence of Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
Cutting speed and feed rate are two critical parameters that dictate how effectively a CNC mill machinist can perform their tasks. The cutting speed refers to how fast the tool moves through the material, while feed rate describes how quickly the workpiece moves under the tool's action. Balancing these two factors ensures efficient removal of material without compromising accuracy.
If you’re wondering whether CNC machining is milling or something else entirely, consider that both cutting speed and feed rate play significant roles in defining how well a job gets done during a milling operation. Too high a speed can lead to overheating or tool failure; too low may result in inefficient machining cycles or poor surface finish quality. Therefore, understanding these dynamics helps refine what is the process of CNC milling into something more predictable and precise.
In practice, optimizing cutting speeds based on material type enables machinists to achieve better results while minimizing wear on tools—an essential consideration for any successful CNC operation.
How Tooling Geometry Impacts Precision
The geometry of tooling used in CNC milling operations cannot be overlooked when discussing accuracy factors. Tool shape affects not only cutting efficiency but also surface finish quality—a key aspect for many projects requiring tight tolerances. Whether you're familiar with what a CNC mill machinist does or just starting out with your own projects, knowing about tooling geometry will elevate your understanding of precision manufacturing.
Different geometries allow for varied engagements with materials; for example, corner radius tools are often used for finishing passes due to their ability to produce smoother surfaces compared to sharp-edged tools that might leave marks or burrs behind. Additionally, correct selection based on application needs helps reduce vibration during operation—another factor influencing overall precision during machining processes like pocketing or drilling within larger projects.
Ultimately, mastering tooling geometry equips machinists with greater control over their workpieces—enhancing not just accuracy but also productivity across all aspects of what is involved in a successful CNC milling operation.
Common CNC Milling Techniques
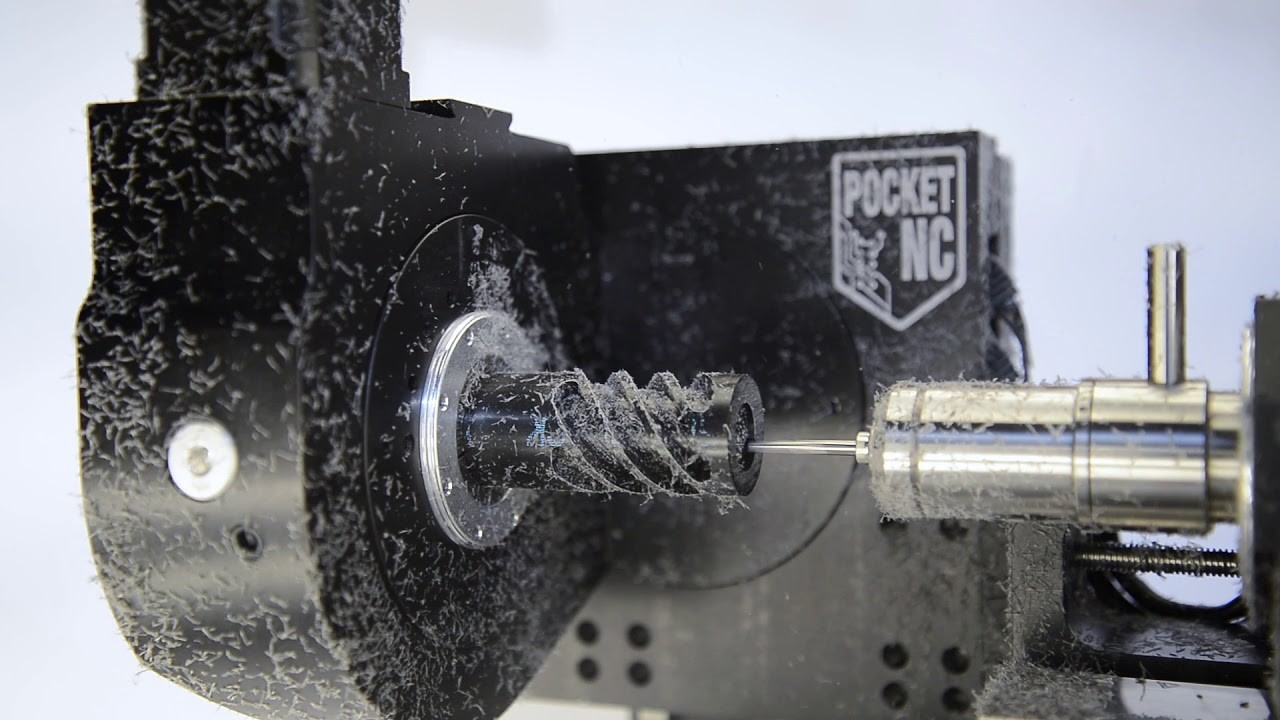
CNC milling operations encompass a variety of techniques designed to achieve specific machining tasks. Understanding these techniques is crucial for anyone involved in the process, whether you’re a seasoned CNC mill machinist or just starting out. Let’s explore some of the most common methods used in CNC milling and how they contribute to the overall effectiveness of the operation.
Face milling vs. contour milling
Face milling and contour milling are two fundamental techniques within the realm of CNC machining that often leave newcomers scratching their heads: Is CNC machining milling? The answer lies in their distinct purposes. Face milling involves cutting flat surfaces and can remove material from a workpiece's surface, while contour milling focuses on shaping complex curves and profiles, allowing for more intricate designs.
In practice, face milling is typically used for producing flat surfaces on parts that require high precision, making it an essential part of the basic CNC milling operation. On the other hand, contour milling shines when dealing with parts that need detailed outlines or contours—think of it as sculpting with metal! Both techniques play vital roles in ensuring that components meet design specifications while maximizing efficiency.
Pocket milling explained
Pocket milling is another key technique employed in CNC machining operations that deserves special attention. So, what is pocket milling? Essentially, it's a method used to create recessed areas or pockets in a workpiece by removing material from inside a defined boundary—perfect for creating spaces where other components will fit snugly.
This technique is particularly useful when working with complex parts where precision matters most; thus, understanding how pocketing contributes to overall accuracy helps any aspiring machinist grasp what is the process of CNC milling? By utilizing specialized tooling and software controls during pocketing operations, machinists can achieve tight tolerances necessary for modern engineering applications.
Drilling and tapping in CNC milling operations
Drilling and tapping are indispensable processes integrated into many CNC milling operations that every machinist should master. Drilling involves creating holes through materials using rotating drill bits while tapping refers to cutting threads inside those holes—essentially preparing them for screws or bolts to ensure proper assembly later on.
These processes are often combined with other techniques like face or contour milling to produce fully functional parts directly from raw stock material—a testament to how versatile a basic CNC milling operation can be! The synergy between drilling and tapping enhances productivity while maintaining accuracy; thus understanding these methods enriches any machinist's skill set significantly as they navigate through various projects.
The Role of a CNC Mill Machinist

In the world of manufacturing, a CNC mill machinist is a pivotal player in executing precision tasks that ensure the efficiency and quality of products. This role involves operating CNC milling machines to create intricate parts from various materials, making it crucial for industries ranging from aerospace to automotive. But what exactly does it mean to be a CNC mill machinist?
What is a CNC mill machinist?
A CNC mill machinist is an individual trained specifically to operate and manage CNC milling machines, which are essential in the machining process. They play a critical role in the overall CNC milling operation by interpreting blueprints, programming machines, and ensuring that parts are produced within specified tolerances. Essentially, they bridge the gap between complex designs and tangible products—making them indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Skills required for effective machining
To thrive as a CNC mill machinist, one must possess a blend of technical skills and practical knowledge about machinery. Understanding how CNC milling works is crucial; this includes familiarity with tooling geometry, cutting speeds, and feed rates that influence the quality of workpieces. Additionally, attention to detail is paramount because even minor errors can lead to significant discrepancies in finished products—so precision is key!
Day-to-day responsibilities of a CNC machinist
On any given day, a CNC mill machinist will engage in various tasks that keep operations running smoothly. These responsibilities include setting up machines for production runs based on specific job requirements and performing regular maintenance checks on equipment to ensure optimal performance. Furthermore, they often conduct quality inspections throughout the machining process to confirm adherence to standards—after all, when it comes down to what is the basic CNC milling operation? It’s all about precision!
Conclusion
In wrapping up our exploration of CNC milling operations, it's clear that precision and skill play pivotal roles. Understanding what is the process of CNC milling? is essential, as it lays the groundwork for mastering this intricate field. From the essential components to the various techniques employed, each aspect contributes to effective machining outcomes.
Recap of CNC Milling Key Factors
Throughout our discussion, we have highlighted several key factors influencing CNC milling operations. The distinction between Is CNC machining milling? and other processes is crucial for clarity in manufacturing environments. Additionally, knowing what is a CNC mill machinist? helps emphasize the importance of skilled professionals who drive these operations with expertise and knowledge.
Importance of Continuous Learning in CNC
In an ever-evolving industry like CNC milling, continuous learning is not just beneficial—it's essential. As technology advances, understanding how CNC milling works becomes increasingly vital to staying competitive. Whether it's keeping up with new software or emerging techniques, ongoing education ensures machinists remain at the forefront of innovation.
Future Trends in CNC Milling Operations
Looking ahead, future trends in CNC milling operations signal exciting developments on the horizon. Automation and AI are set to revolutionize how we approach basic CNC milling operations, increasing efficiency while reducing human error. Embracing these changes will be key for manufacturers aiming to optimize their workflows and maintain a competitive edge.

