Introduction

In the ever-evolving world of manufacturing, the choice between CNC machining and injection molding can significantly impact production efficiency, cost, and product quality. With a myriad of options available, understanding what sets these two methods apart is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. This comparison not only helps in answering questions like What is the difference between CNC machining and injection molding? but also guides manufacturers toward making informed decisions that align with their goals.
Understanding CNC Machining and Injection Molding
CNC machining involves using computer-controlled tools to remove material from a solid block, creating precise parts with exceptional detail. On the other hand, injection molding is a process where molten material is injected into molds to form complex shapes quickly and efficiently. Both methods have unique strengths; however, knowing what is the difference between molding and machining? can help manufacturers select the best approach for their specific needs.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Method
Selecting between CNC machining vs injection molding can have lasting effects on production timelines and costs. The right choice often hinges on factors such as volume requirements, material types, and design complexities. Furthermore, understanding whether is injection molding cheaper than machining? can lead to significant savings in both time and resources.
Why This Comparison Matters
As industries continue to innovate and evolve, comparing these two manufacturing techniques becomes increasingly relevant for businesses seeking competitive advantages. By evaluating aspects like cost efficiency, precision tolerances, material versatility, production speed, and overall suitability for various applications, manufacturers can make strategic decisions that enhance productivity. Ultimately, this comparison empowers companies to ask not just what is better than injection molding? but also how they can leverage both methods effectively in their operations.
Overview of CNC Machining
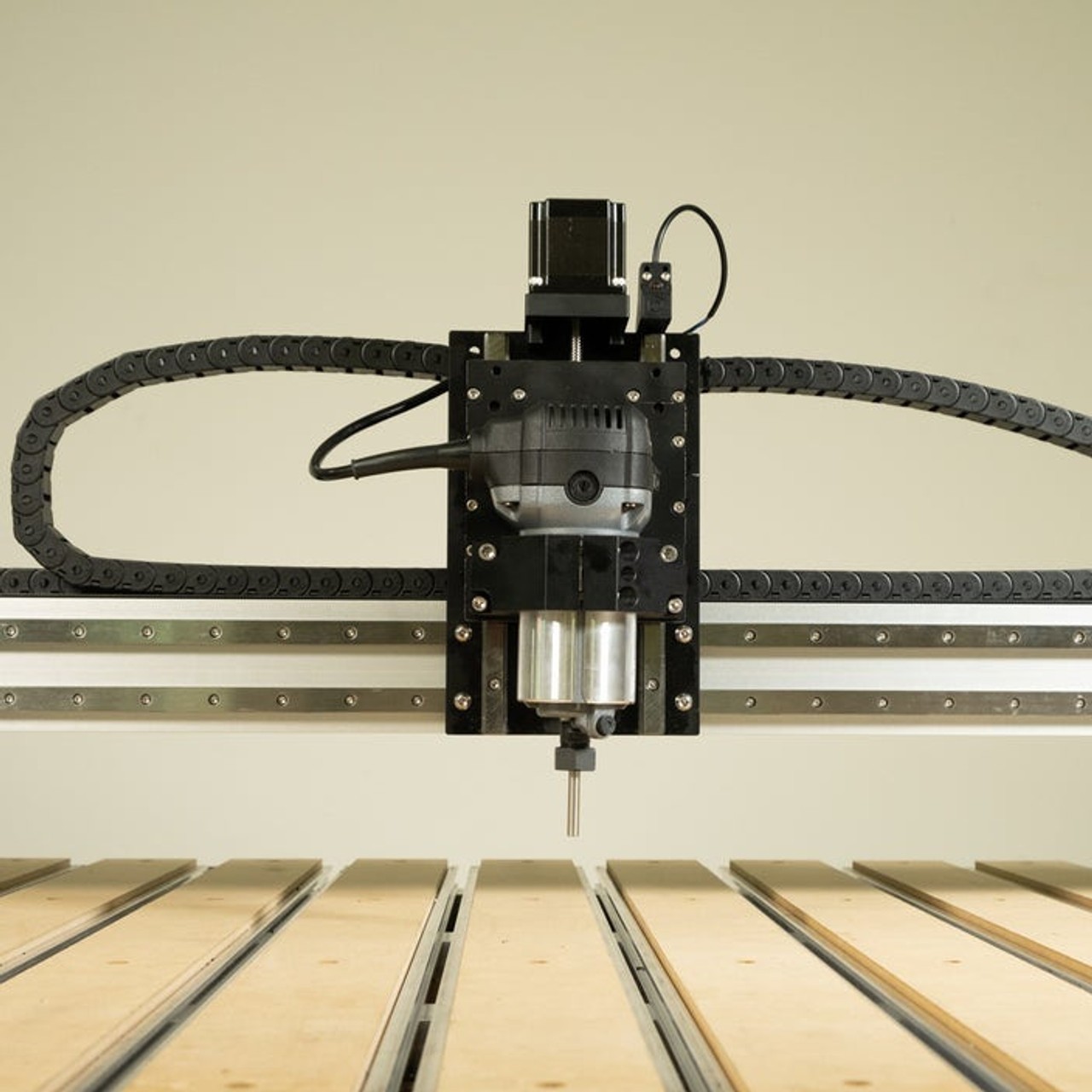
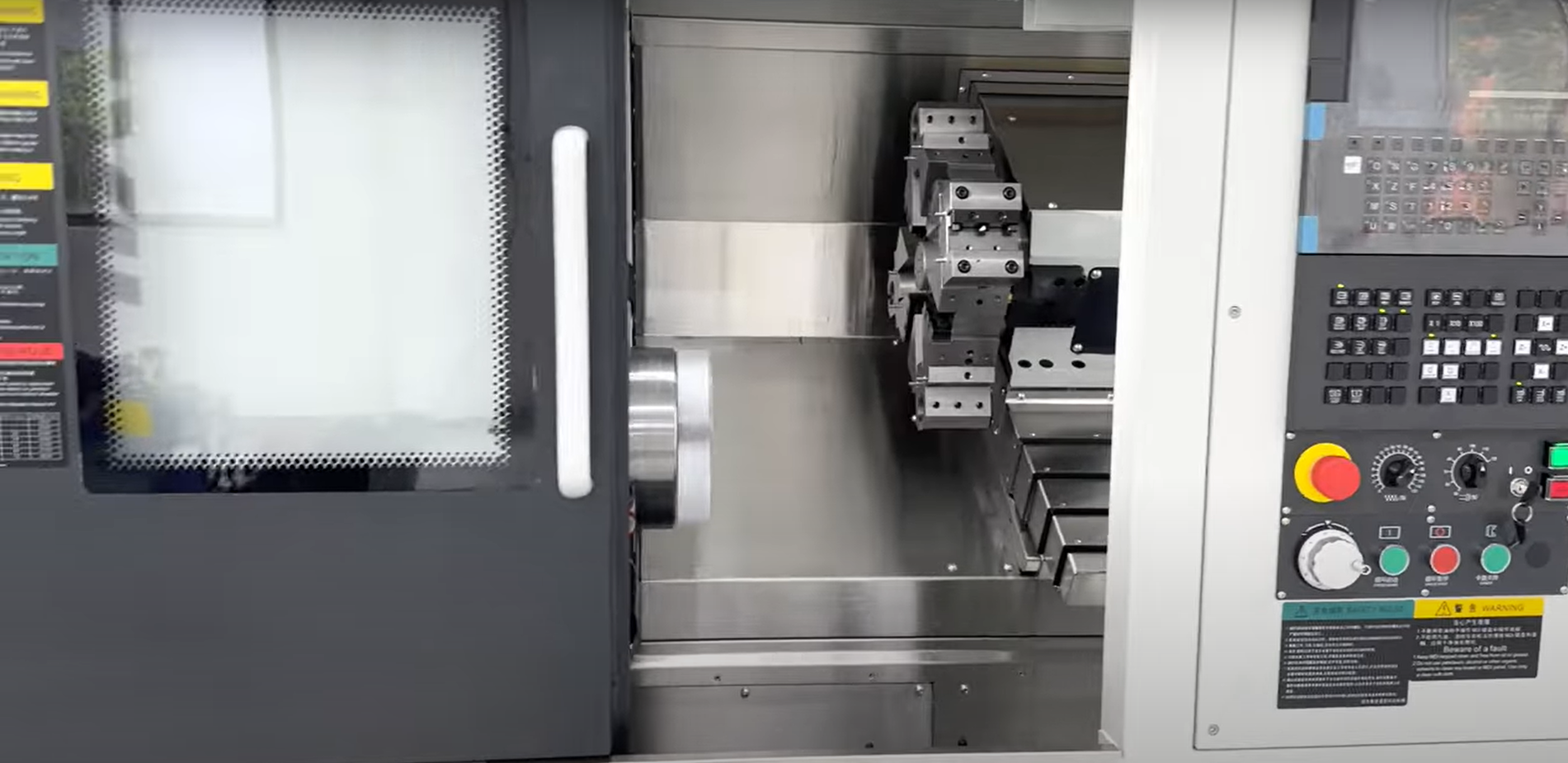
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that utilizes computer numerical control to create precise components from various materials. This method involves the use of pre-programmed software to dictate the movement of machinery, allowing for high levels of accuracy and repeatability. Understanding CNC machining is essential when comparing it to other methods, such as injection molding, especially when considering factors like cost, precision, and material versatility.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining stands for Computer Numerical Control machining, a process that automates the operation of machine tools through computer programming. Unlike traditional machining methods that rely on manual adjustments, CNC machining allows for intricate designs and specifications to be executed with minimal human intervention. This technological advancement has revolutionized manufacturing by providing consistency and efficiency in creating complex parts.
Key Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining finds its application across a wide array of industries including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices. For instance, it is often used to produce components like engine parts in the automotive sector or intricate surgical instruments in healthcare. The versatility in applications makes it a preferred option when precision engineering is paramount—a stark contrast when you consider CNC machining vs injection molding.
Advantages of CNC Machining
One major advantage of CNC machining lies in its ability to produce highly precise components with tight tolerances—often better than those achievable through injection molding. Additionally, this method allows for flexibility in design changes without significant retooling costs or time delays; if you need a modification after production begins, it's typically easier with CNC than with molding processes. Furthermore, while many wonder if injection molding is cheaper than machining for mass production scenarios, the upfront costs associated with setting up molds can make CNC more appealing for smaller runs or custom projects.
Overview of Injection Molding

Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create complex shapes and parts. This method is widely used due to its efficiency and ability to produce high volumes of identical items with precision. When considering CNC machining vs injection molding, it's essential to understand the unique characteristics that make injection molding an attractive option for many industries.
What is Injection Molding?
At its core, injection molding is all about shaping materials—typically plastics—by forcing them into a pre-designed mold cavity under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected, ready for use or further processing. So, what is the difference between CNC machining and injection molding? While CNC machining removes material from a solid block to create parts, injection molding builds parts from scratch using liquid materials.
Understanding these processes can help clarify why businesses might choose one method over the other based on their specific needs. For instance, if you're looking for mass production with consistent quality and lower costs per unit, injection molding may be your go-to choice. On the other hand, if you need complex geometries or prototypes in smaller quantities, CNC machining could be more suitable.
Industries That Benefit from Injection Molding
Many industries reap significant benefits from using injection molding as their primary manufacturing method. The automotive sector frequently relies on this technique for producing durable components like dashboards and bumpers in large quantities with tight tolerances. Additionally, consumer goods companies use injection molded parts for everything from toys to kitchenware due to their efficiency in producing high volumes quickly.
Medical device manufacturers also find value in this process because it allows them to create intricate designs while adhering to strict regulatory standards. Moreover, electronics companies benefit from injection molding by producing lightweight housings that protect sensitive components without sacrificing performance or aesthetics. In summary, various sectors thrive on what injection molding offers—high-volume production combined with flexibility.
Advantages of Injection Molding
One of the standout advantages of injection molding lies in its cost-effectiveness when it comes to large-scale production runs—so much so that many often wonder: Is injection molding cheaper than machining? The answer typically leans toward yes; once initial tooling costs are covered (which can be substantial), each additional unit produced tends to be less expensive than those made via CNC machining methods.
In conclusion, understanding these aspects of injection molding helps clarify why it's often favored over CNC machining for certain projects while also highlighting its strengths across various industries—from automotive to consumer goods and beyond.
Comparing Cost Efficiency

Is Injection Molding Cheaper than Machining?
The age-old debate of CNC machining vs injection molding often centers around cost; many wonder, Is injection molding cheaper than machining? Generally speaking, for high-volume production runs, injection molding tends to be more economical due to its ability to produce large quantities quickly and efficiently. However, for low-volume projects or one-off prototypes, CNC machining may prove more cost-effective since it avoids the hefty upfront costs associated with mold creation.
It's essential to consider that while initial setup costs for injection molding can be significant—due to mold design and fabrication—the per-unit cost decreases dramatically with higher volumes. In contrast, CNC machining often incurs lower initial costs but can become expensive on a per-piece basis if you require numerous units. Thus, the answer hinges on your specific manufacturing needs and scales.
Breakdown of Costs in CNC Machining vs Injection Molding
To truly grasp what is the difference between CNC machining and injection molding in terms of costs, we need to break down their respective expenses. For CNC machining, costs include machine time (which varies based on complexity), labor rates (often higher due to skilled operators), and material expenses that can fluctuate based on type and availability.
On the flip side, injection molding involves significant upfront investments in molds—these can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands depending on complexity—but once created, they allow for rapid production at a lower per-unit cost over time. This means that while your initial investment might be steep with injection molding compared to traditional machining processes, the long-term savings can be substantial if you're producing large quantities.
Factors Influencing Manufacturing Costs
Several factors influence manufacturing costs in both methods when considering what is better than injection molding or CNC machining for your project needs. For instance, material choice plays a pivotal role; certain plastics used in injection molding may offer lower prices but could also limit performance characteristics compared to metals utilized in CNC processes.
Additionally, production volume significantly impacts overall expenses—higher volumes generally favor injection molding due to reduced per-unit costs after mold creation recoups its investment over time. Other considerations include lead times; longer lead times associated with custom molds might not suit urgent projects where quick turnarounds are crucial.
Precision and Tolerances

What is the Difference between Molding and Machining?
The primary distinction between molding and machining lies in their methodologies. CNC machining involves cutting away material from a solid block to create the desired shape, allowing for intricate designs with exceptional precision. In contrast, injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold where it cools and solidifies, which can lead to variations in dimensions due to factors like temperature fluctuations and cooling rates—this brings us back to our original question: what is the difference between molding and machining? While both processes aim for accuracy, CNC machining generally offers tighter tolerances than injection molding.
Comparing Tolerances of CNC Machining and Injection Molding
When comparing tolerances of CNC machining vs injection molding, it's crucial to note that CNC machines can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches or even better depending on the application. On the other hand, injection molding typically operates within a range of ±0.005 inches to ±0.020 inches due to its reliance on molds that may wear over time or be affected by thermal expansion during production runs. This discrepancy raises an important question: Is injection molding cheaper than machining? While it might be more cost-effective for large volumes, if precision is paramount for your project, investing in CNC machining could save you headaches down the line.
Real-World Examples of Precision Applications
Real-world applications showcase how precision influences industry choices between these two methods. For instance, industries like aerospace or medical devices often require components with extremely tight tolerances; hence they lean towards CNC machining when crafting parts such as turbine blades or surgical instruments—demonstrating that when it comes down to quality versus quantity, what is better than injection molding might just be good old-fashioned machining! Conversely, consumer electronics frequently utilize injection molded parts due to high-volume production needs coupled with acceptable tolerances; think smartphone casings that don't require ultra-fine details but need consistent shapes across thousands of units.
Material Versatility

Material Options in CNC Machining
CNC machining stands out for its ability to work with a wide variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This flexibility allows manufacturers to produce parts that require specific properties, such as high strength or heat resistance, making it ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive. Additionally, because CNC machining involves cutting away material from a solid block, there are virtually no limitations on the types of materials that can be utilized—if you can get it in a block or sheet form, chances are you can machine it.
In contrast to injection molding's reliance on pre-formed pellets or granules of plastic, CNC machining opens up a world of possibilities for custom and exotic materials. Whether you’re looking at aluminum alloys or engineering-grade plastics like PEEK and Nylon 6/6, CNC machining gives you the freedom to choose the best material for your application without being restricted by mold constraints. This is crucial when considering factors such as durability or weight—elements that often dictate project success.
Material Considerations for Injection Molding
Injection molding typically utilizes thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers that are melted down and injected into molds under high pressure. While this process is efficient for mass production runs with consistent quality across large quantities, it does limit the variety of materials available compared to CNC machining. The choice of materials also hinges on considerations like flow characteristics during injection and cooling rates post-molding; these factors influence cycle times and final part properties.
Moreover, many modern injection molders are now experimenting with composite materials and specialty plastics designed to enhance performance characteristics like toughness or temperature resistance. However, when comparing CNC machining vs injection molding in terms of material versatility alone, it's clear that while injection molding is excellent for producing uniform parts at scale using specific types of plastics, it doesn't quite match the breadth available through CNC processes.
What is Better than Injection Molding for Material Variety?
So if we’re asking what is better than injection molding regarding material variety? The answer leans heavily towards CNC machining due to its extensive range of workable materials beyond just plastics—think metals like titanium or even wood composites! As industries demand more specialized components tailored precisely to their needs (think medical devices requiring biocompatible materials), CNC machining emerges as an attractive alternative due to its adaptability.
Furthermore, while some may argue about cost implications—Is injection molding cheaper than machining?—the answer often depends on volume requirements rather than sheer material choice alone. In short: if your project demands diverse material options without sacrificing quality or precision over different production runs, CNC machining takes the cake every time!
Production Volume and Speed

CNC Machining for Small Batches
CNC machining is often the go-to choice for small batch productions due to its flexibility and precision. When you're asking yourself, What is the difference between CNC machining and injection molding? consider that CNC allows for quick adjustments in design without the need for expensive molds. This adaptability makes it ideal for prototypes or low-volume runs, where rapid iterations are necessary without breaking the bank.
In addition to flexibility, CNC machining offers high precision that smaller batches often require. It can produce intricate designs with tight tolerances that might be challenging or costly with injection molding methods. Therefore, if you’re working on a project where quality trumps quantity, CNC machining could be your best bet.
Injection Molding for Mass Production
On the other hand, when it comes to mass production, injection molding takes the crown. This process is designed to create large quantities of identical parts quickly and efficiently after an initial setup cost for molds has been covered. If you've ever wondered if injection molding is cheaper than machining in bulk scenarios, the answer typically leans towards yes—especially when producing thousands of units.
The efficiency of injection molding lies not only in its ability to produce high volumes but also in its speed; once a mold is created, parts can be produced rapidly with minimal downtime between cycles. This makes it particularly appealing for industries like automotive or consumer goods that demand consistent quality at scale. So if you're looking at projects requiring high output over time, injection molding may be what you're after.
Speed Comparisons and Lead Times
When comparing speed between these two manufacturing methods—CNC machining vs injection molding—the differences become quite pronounced based on production needs and volume requirements. For small batches using CNC machining, lead times can vary depending on complexity but generally remain swift due to direct programming from CAD files without extensive setup times like those required for creating molds in injection molding.
Conversely, once molds are established in an injection mold setup—albeit a lengthy initial phase—the actual cycle time per part becomes remarkably quick compared to individual CNC operations per piece produced one at a time. This means that while initial lead times may favor CNC machining during prototyping phases or low-volume needs, long-term projects requiring mass production will benefit from the rapid throughput offered by injection molding processes.
In conclusion, understanding what is better than injection molding depends heavily on your specific needs regarding volume and speed; both methods have their unique advantages depending on your project requirements.
Conclusion

In the world of manufacturing, the choice between CNC machining vs injection molding can significantly impact your project’s success. Each method boasts its own set of advantages and ideal applications, making it crucial to understand what is the difference between CNC machining and injection molding. By examining aspects such as cost efficiency, precision, material versatility, and production volume, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs.
Recap of Key Differences and Advantages
CNC machining offers unparalleled precision and flexibility in working with a variety of materials. It is particularly advantageous for low-volume production runs or highly detailed components where tight tolerances are essential. On the other hand, injection molding shines in high-volume production scenarios where speed and cost-effectiveness are paramount; thus answering the question: is injection molding cheaper than machining? The answer often leans towards yes, especially when producing large quantities.
When to Choose CNC Machining
If your project requires intricate designs or customized parts in smaller quantities, CNC machining is likely your best bet. This method allows for quick adjustments without significant downtime or retooling costs, making it perfect for prototypes or specialized components. In contrast to injection molding's longer setup times and higher initial costs, CNC machining provides a more agile approach that can adapt to changing requirements.
Final Thoughts on Injection Molding vs CNC Machining
Ultimately, the decision between injection molding and CNC machining boils down to specific project needs and constraints. While both methods have their merits, understanding what is better than injection molding depends on factors like production volume and required precision levels. Remember that each process serves unique purposes; thus weighing their advantages will help you navigate this complex landscape effectively.

